Iron chelation therapy
Iron chelation therapy is vital in medical treatment to remove excess iron from the body, especially in people with conditions like thalassemia major, sickle cell disease, and other chronic anemias requiring frequent blood transfusions. These transfusions are necessary to maintain sufficient hemoglobin and red blood cell levels, but it can lead to the accumulation of excess iron in the body. Globally, hemoglobin-related disorders affect about 7.0% of the population, with sickle cell anemia comprising roughly 70.0% of cases and the remainder suffering from thalassemia or other blood disorders. Thalassemia, which affects approximately 2.1% of the global population, is a significant concern.
Understanding Thalassemia
Thalassemia, a hereditary condition caused by gene mutations affecting hemoglobin production, disrupts the protein's normal structure in red blood cells. Hemoglobin, comprising two alpha and two beta protein chains, is crucial for oxygen transport in the body. When either alpha or beta chain production is impaired in thalassemia, oxygen delivery becomes insufficient, leading to anemia and related health issues. This genetic anomaly results from inheriting defective genes from both parents, leading to conditions like alpha thalassemia, beta thalassemia, or other hemoglobinopathies like Hemoglobin E Beta Thalassemia.
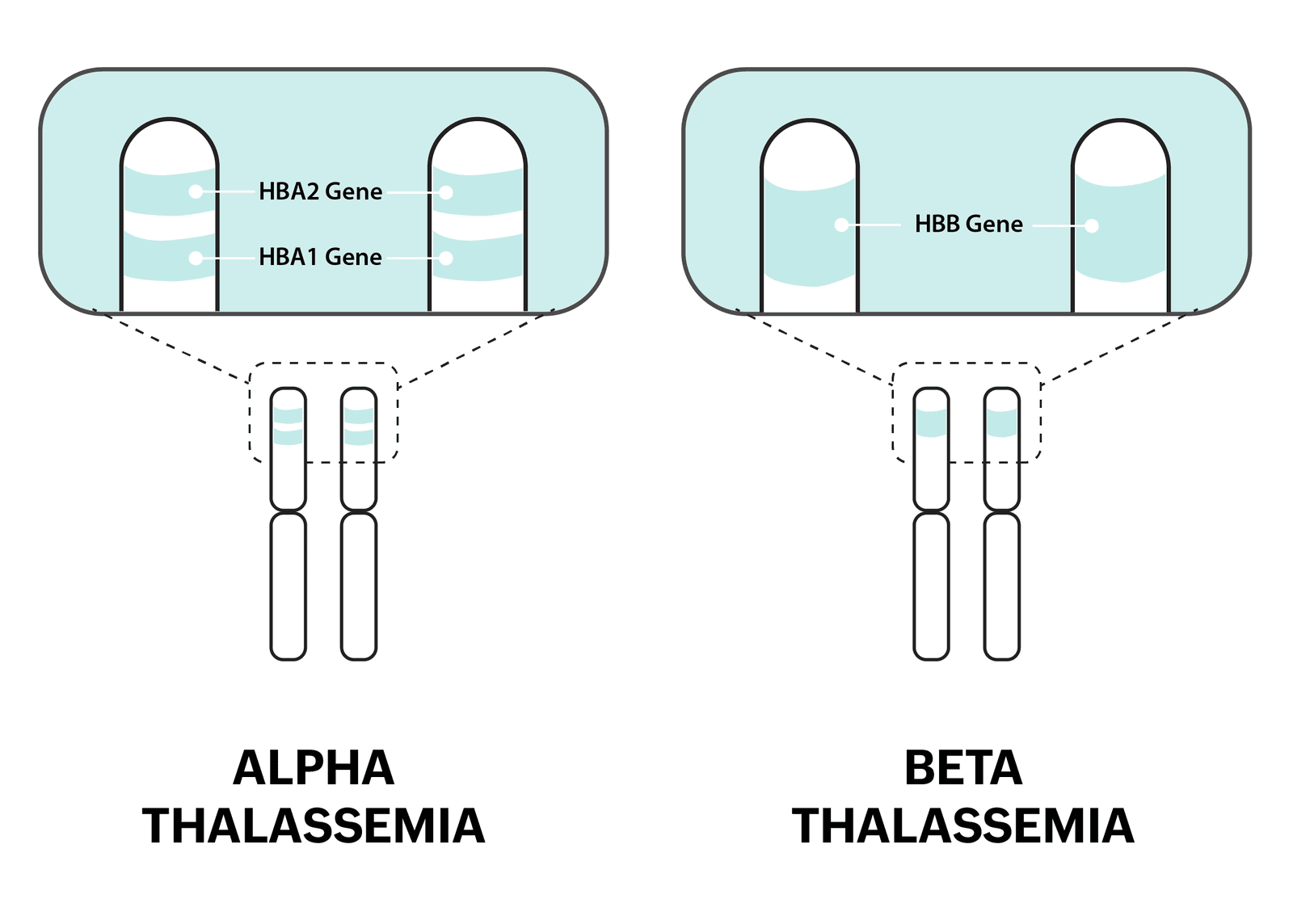
Treatment typically involves regular blood transfusions to replenish red blood cells and alleviate anemia. However, frequent transfusions can cause iron overload, risking organ damage. Iron chelation therapy is crucial in managing thalassemia by removing excess iron from the body, thereby preventing complications.
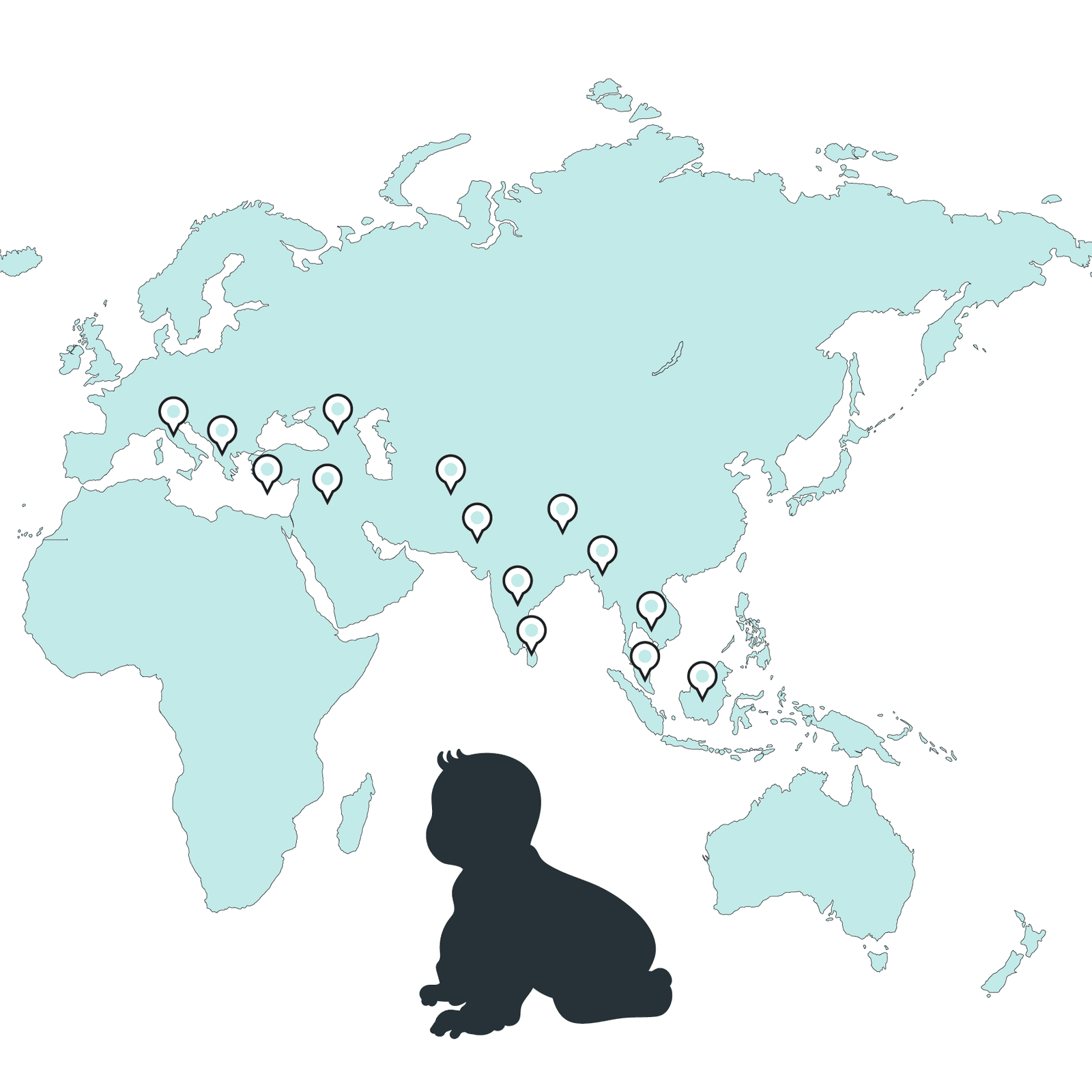
India registers the highest count of children diagnosed with Thalassemia major, estimated to range between 100,000 to 150,000 cases, with approximately 10,000 to 15,000 new cases emerging annually. Thalassemia is also prevalent in various regions, including Greece, coastal Turkey, parts of Italy, major Mediterranean islands like Cyprus, Middle Eastern nations, Southeast Asia, and South Asian countries. In the United States, thalassemia is considered a rare disease, impacting fewer than 20,000 individuals.
Iron chelation Therapy : Iron chelation therapy entails administering chelating agents like Desferal (deferoxamine) to remove excess iron from the body. These chelators bind to iron molecules, facilitating iron excretion through urine, thereby reducing iron levels and lowering the risk of organ damage, particularly to the heart and liver. Following each blood transfusion, it's crucial to monitor the patient's ferritin level because each unit of transfused red blood cells contains around 200 milligrams of elemental iron. Ferritin, a biomarker indicating iron stores in the body, can be assessed through a Ferritin Blood Test, with elevated levels indicating iron overload. In such cases, iron chelation therapy is vital, especially for individuals with thalassemia who regularly undergo blood transfusions. Deferoxamine can swiftly decrease ferritin levels, but careful monitoring is necessary to prevent toxicity-related complications and ensure a gradual reduction in iron levels. Typically, deferoxamine is administered as a 12-hour infusion on five nights a week.
Managing Iron Overload Before Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT):
Bone marrow transplant (BMT) offers hope for severe cases of beta-thalassemia by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with stem cells from a compatible donor. However, clinicians often face a significant challenge in managing iron overload prior to BMT, which could delay the surgery. While oral medications for iron chelation therapy are effective, they usually take several months to lower iron levels sufficiently. Hence, patients scheduled for BMT should initiate syringe infusion pump therapy at least two months prior to the procedure to achieve ferritin levels below 500.
Clinical Approaches to Iron Chelation Therapy : Methods and Considerations
Oral Iron chelation Therapy : Oral chelators like deferasirox and deferiprone are commonly used for iron overload management to reduce ferritin levels in patients with iron overload. These medications function by binding to excess iron, aiding its elimination through urine and feces. However, the reduction in ferritin levels may be slower compared to IV chelation therapy. It's important for individuals considering this therapy to discuss its potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
These oral medications may lead to gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and alterations in taste. These adverse effects can significantly impact the patient's quality of life and may even prompt treatment discontinuation or necessitate dose adjustments. Consequently, the time required to achieve the desired iron levels may be further prolonged.

IV chelation therapy : IV chelation therapy is pivotal in managing iron overload in thalassemia patients, administered directly into the bloodstream through intravenous infusion. Research and clinical experience confirm its effectiveness in reducing ferritin levels. However, the therapy's infusion times can be prolonged, spanning from several hours to overnight. Regular monitoring of ferritin levels is necessary but can be burdensome, disrupting daily activities.
Subcutaneous iron chelation therapy : Subcutaneous Infusion Involves injecting chelating agents under the skin (subcutaneously) using a small portable pump, enabling patients to self-administer therapy at home. This approach can be as effective as IV therapy in reducing iron overload and lowering ferritin levels, while also improving patient compliance and quality of life.
Challenges in India:
In India, patients often rely on desferal syringe infusion pumps for their treatment. While effective, these pumps come with significant financial burdens for patients and their families due to their elevated costs. Additionally, sourcing these pumps from overseas presents challenges in obtaining necessary support services and product assistance. Issues such as delays in servicing, difficulties in procuring replacement parts, and a lack of locally available customer support complicate and hinder effective treatment for patients.
The Accuflow Thala Pump enables patients to seamlessly integrate therapy into their daily lives, fostering a sense of normalcy and allowing them to engage fully in personal and professional activities. With a focus on accessibility, our pump is easily accessible to patients, reducing reliance on imported devices and ensuring affordability for a wider population. Additionally, our dedicated support services guarantee timely maintenance, troubleshooting, and access to replacement parts, providing a holistic solution to optimize care for thalassemia patients and improve their quality of life.
By addressing concerns of accessibility and affordability, the Accuflow Thala Pump streamlines thalassemia management, empowering patients to take control of their health journey with confidence and dignity. Through collaborative efforts and innovative initiatives, we aim to ensure comprehensive care for all individuals affected by thalassemia, irrespective of geographical or economic constraints.
Iron chelation therapy
Iron chelation therapy is a crucial medical intervention used to eliminate excess iron from the body, particularly in individuals with conditions such as thalassemia major, sickle cell disease, and other chronic anemia that require frequent blood transfusions. These transfusions, essential for maintaining sufficient hemoglobin and red blood cell levels, can lead to the accumulation of excess iron in the body. About 7.0% of the global population is affected by hemoglobin-related disorders, with sickle cell anemia representing approximately 70.0% of cases, while the rest suffer from thalassemia or other blood disorders. Thalassemia, affecting approximately 2.1% of the global population, is a significant concern.

Understanding Thalassemia
Thalassemia, a hereditary condition caused by gene mutations affecting hemoglobin production, disrupts the protein's normal structure in red blood cells. Hemoglobin, comprising two alpha and two beta protein chains, is crucial for oxygen transport in the body. When either alpha or beta chain production is impaired in thalassemia, oxygen delivery becomes insufficient, leading to anemia and related health issues. This genetic anomaly results from inheriting defective genes from both parents, leading to conditions like alpha thalassemia, beta thalassemia, or other hemoglobinopathies like Hemoglobin E Beta Thalassemia.

Treatment typically involves regular blood transfusions to replenish red blood cells and alleviate anemia. However, frequent transfusions can cause iron overload, risking organ damage. Iron chelation therapy is crucial in managing thalassemia by removing excess iron from the body, thereby preventing complications.

Iron chelation Therapy
Iron chelation therapy entails administering chelating agents like Desferal (deferoxamine) to remove excess iron from the body. These chelators bind to iron molecules, facilitating iron excretion through urine, thereby reducing iron levels and lowering the risk of organ damage, particularly to the heart and liver. Following each blood transfusion, it's crucial to monitor the patient's ferritin level because each unit of transfused red blood cells contains around 200 milligrams of elemental iron. Ferritin, a biomarker indicating iron stores in the body, can be assessed through a Ferritin Blood Test, with elevated levels indicating iron overload. In such cases, iron chelation therapy is vital, especially for individuals with thalassemia who regularly undergo blood transfusions. Deferoxamine can swiftly decrease ferritin levels, but careful monitoring is necessary to prevent toxicity-related complications and ensure a gradual reduction in iron levels. Typically, deferoxamine is administered as a 12-hour infusion on five nights a week.

Managing Iron Overload Before
Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT):
Bone marrow transplant (BMT) offers hope for severe cases of beta-thalassemia by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with stem cells from a compatible donor. However, clinicians often face a significant challenge in managing iron overload prior to BMT, which could delay the surgery. While oral medications for iron chelation therapy are effective, they usually take several months to lower iron levels sufficiently. Hence, patients scheduled for BMT should initiate syringe infusion pump therapy at least two months prior to the procedure to achieve ferritin levels below 500.
Clinical Approaches to Iron Chelation Therapy : Methods and Considerations

Oral Iron chelation Therapy : Oral chelators like deferasirox and deferiprone are commonly used for iron overload management to reduce ferritin levels in patients with iron overload. These medications function by binding to excess iron, aiding its elimination through urine and feces. However, the reduction in ferritin levels may be slower compared to IV chelation therapy. It's important for individuals considering this therapy to discuss its potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
These oral medications may lead to gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and alterations in taste. These adverse effects can significantly impact the patient's quality of life and may even prompt treatment discontinuation or necessitate dose adjustments. Consequently, the time required to achieve the desired iron levels may be further prolonged.

